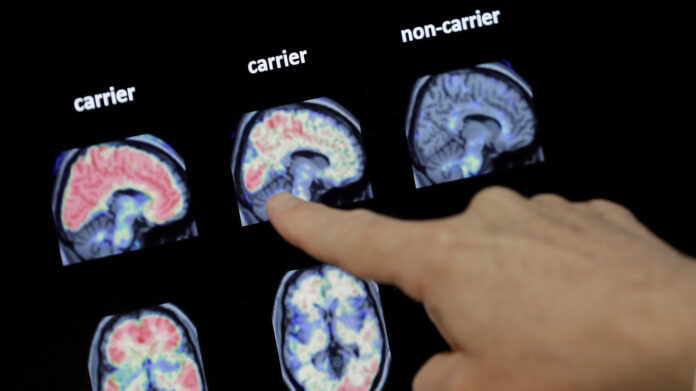
Scientists say analysis into Alzheimer’s must take a broader view of how the illness impacts the mind — whether or not that is modifications within the cortex or the function of irritation.
Matt York/AP
conceal caption
toggle caption
Matt York/AP
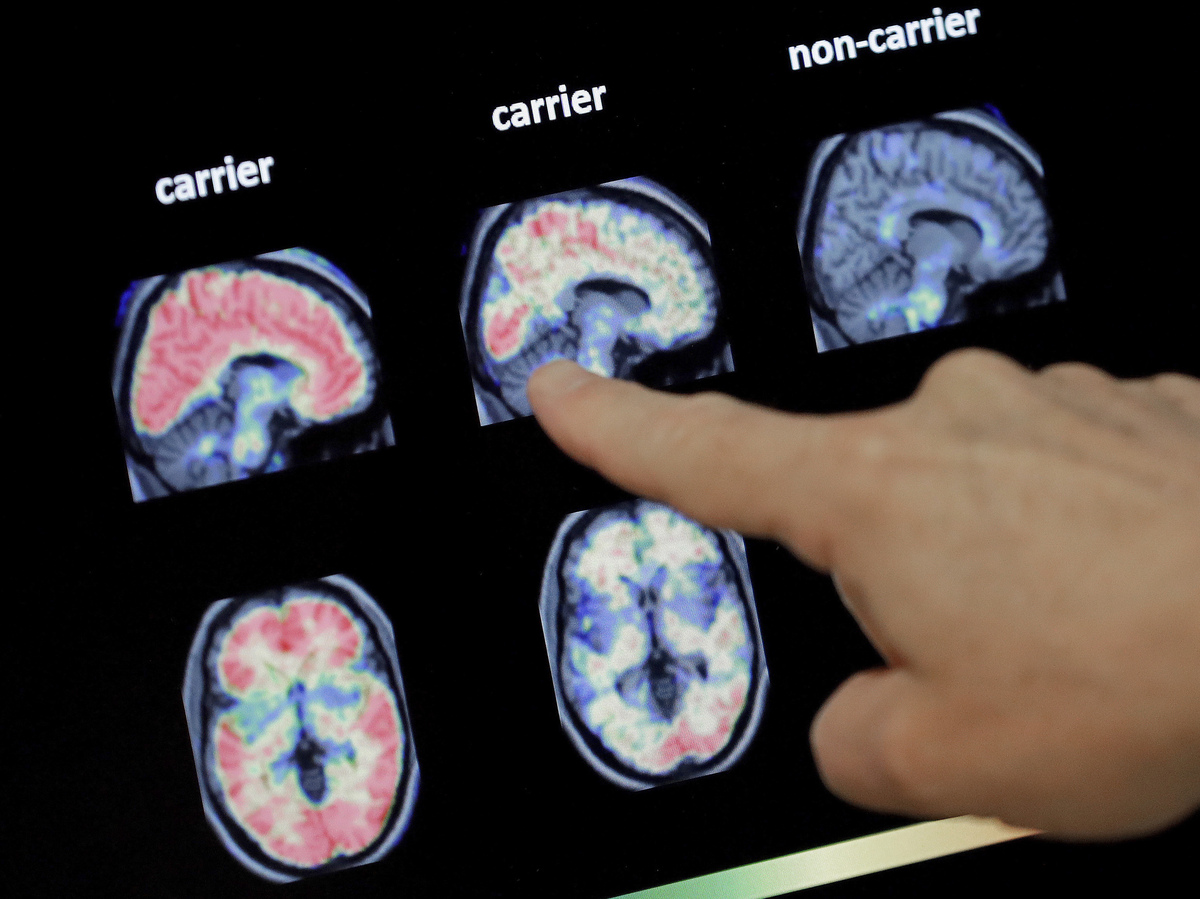
Scientists say analysis into Alzheimer’s must take a broader view of how the illness impacts the mind — whether or not that is modifications within the cortex or the function of irritation.
Matt York/AP
The sector of Alzheimer’s analysis is branching out.
After many years of specializing in the sticky amyloid plaques and tangled tau fibers related to the illness, mind researchers are looking for different potential causes of impaired reminiscence and pondering.
That search is on full show this week on the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference in San Diego, the place classes are exploring components together with genes, mind damage, clogged arteries and irritation.
A gaggle of researchers from Seattle even unveiled a extremely detailed atlas displaying how several types of mind cells change in Alzheimer’s. The objective is to assist scientists establish new approaches to therapy.
“Definitely, plaques and tangles are an indicator,” says Maria Carrillo, chief science officer of the Alzheimer’s Affiliation. “It does not imply plaques are the reason for cell dying.”
Plaques are clumps of a protein referred to as beta-amyloid that seem within the areas between neurons. Tangles are made up of a protein referred to as tau that seems inside a neuron.
Each proteins are likely to accumulate within the brains of individuals with Alzheimer’s. However their function in killing mind cells continues to be unclear.
Carrillo says the Alzheimer’s area must look to most cancers analysis the place a deeper understanding of the illness has led to raised therapies.
The shift comes after a sequence of experimental medicine have succeeded in eradicating amyloid plaques and tau tangles from the mind, however did not halt the illness.
The Meals and Drug Administration has authorised one amyloid drug, Aduhelm, however continues to be evaluating whether or not it truly helps sufferers.
An Alzheimer’s Atlas
The research that produced the atlas is emblematic of how researchers are recalibrating.
“What we’re making an attempt to do with this research is to take a look at cell vulnerability early on in illness, earlier than [people] have plaques and tangles, earlier than they’ve cognitive impairment,” says Dr. C. Dirk Keene, a neuropathologist on the College of Washington.
To create the atlas, Keene and a workforce of researches analyzed greater than one million cells from 84 brains donated by individuals who’d signed up for Alzheimer’s analysis initiatives run by the College of Washington and Kaiser Permanente Washington Analysis Institute.
The brains got here from donors “in any respect completely different phases of illness” Keene says, “so we are able to pinpoint what’s taking place from the earliest ranges right through to folks with superior illness.”
The hassle is funded by the Nationwide Institute on Growing old and grew out of the federal BRAIN initiative launched by President Obama in 2013.
The atlas got here from the conclusion that “If we wish to deal with ailments of an especially complicated mobile organ, you have to perceive that organ significantly better than we do,” says Ed Lein, a senior investigator on the Allen Institute for Mind Science, which performed a key function in analyzing the mind tissue.
So the workforce spent years learning cells in wholesome brains earlier than brains affected by Alzheimer’s.
“We have outlined what a standard grownup mind seems like,” Lein says, “and now we are able to use that information and search for modifications which might be taking place in particular sorts of cells.”
Discovering susceptible mind cells
On the Alzheimer’s assembly, the workforce described modifications they noticed in additional than 100 forms of cells taken from the cortex — an space of the mind which is vital to reminiscence and pondering.
One discovering was that neurons that make connections inside the cortex itself had been more likely to die than those who connect with distant areas of the mind.
“What we’re seeing is a profound impact on cortical circuitry that very plausibly is the rationale we now have cognitive decline,” Lein says.
If that’s the case, a therapy designed to guard these susceptible neurons would possibly forestall declines in reminiscence and pondering linked to Alzheimer’s.
The workforce additionally discovered a proliferation of mind cells that contribute to irritation. These included sure immune cells and a sort of cell that responds to damage.
“So whereas the neurons are misplaced, the non-neuronal cells are literally rising and altering” Lein says.
The discovering helps the concept irritation performs an vital function in Alzheimer’s, and that anti-inflammatory medicine would possibly assist shield the mind.
The Seattle workforce hopes different scientists will use the mind cell atlas to provide you with new therapies for Alzheimer’s.
“We have created an open-access useful resource the place the entire group can come and take a look at this knowledge,” Lein says. “They’ll mine it to hurry up progress within the area as a complete.”
Rushing up progress is one cause Kyle Travaglini, a researcher on the Allen Institute, jumped on the probability to work on the Alzheimer’s venture.
“My grandmother began growing Alzheimer’s illness once I was simply going off to varsity,” says Travaglini, who acquired his PhD in 2021.
Travaglini says the atlas venture is interesting as a result of it is not based mostly on a preconceived thought about what causes Alzheimer’s.
“It is like trying on the identical illness that everybody has been however in a wholly completely different approach,” he says.